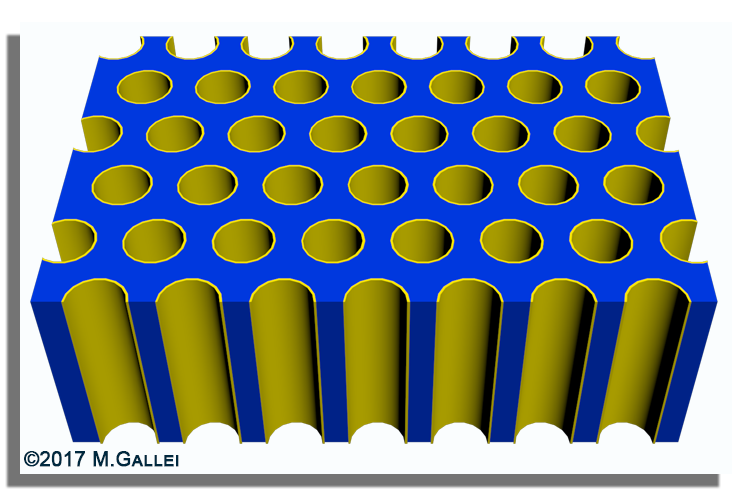
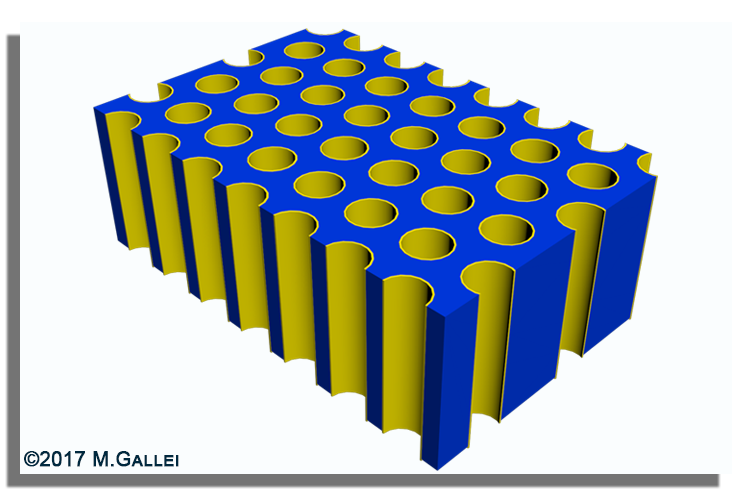
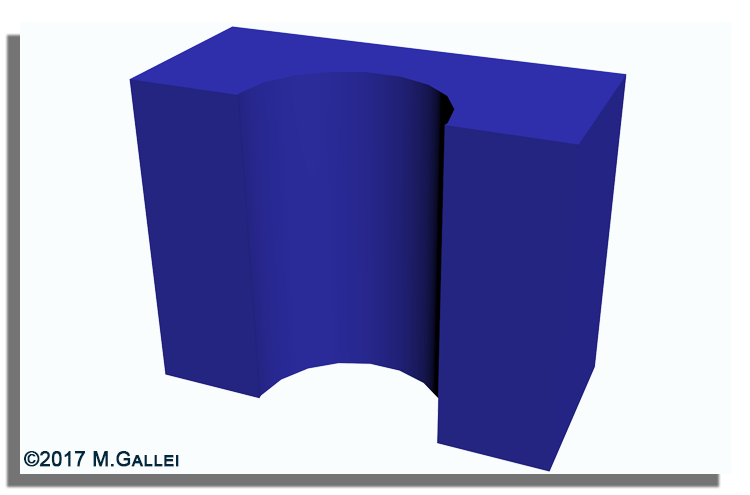
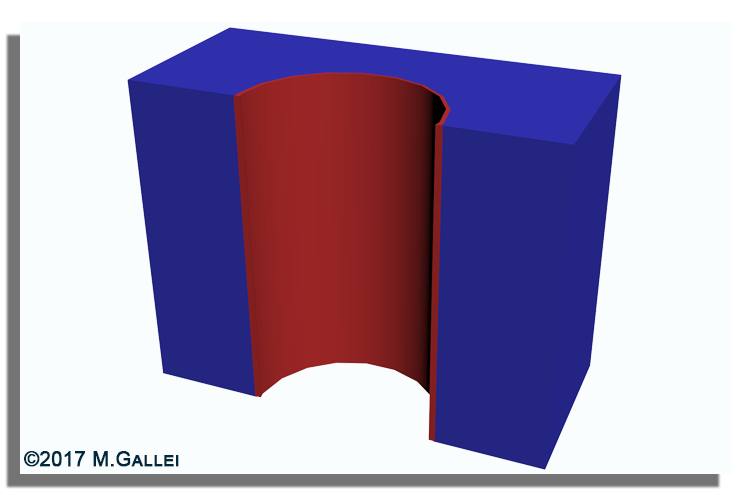
In the field of separation processes, immobilized functional polymers, block copolymer or inverse opal structures attracted enormous attention as potential filtration membranes.
In our group we investigate the usability of tailor-made polymer architectures based on block copolymers or core/shell particles for the preparation of hierarchically structured porous materials featuring various functional groups.
One concept focusses on the self-assembly and phase inversion of amphiphilic polymers while the other concept is based on the melt-shear organization technique followed by core particle removal.
These porous free-standing hybrid or polymer-based film materials are potential candidates for smart switchable membranes, optical sensors and catalyst supports.
Exemplary references:
- Schäfer, C. G.; Winter, T.; Heidt, S.; Dietz, C.; Ding, T.; Baumberg, J. J.; Gallei, M. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, (10), 2204-2214.
- Schöttner, S.; Schaffrath, H.-J.; Gallei, M. Macromolecules 2016, 49, (19), 7286-7295.
- Rüttiger, C.; Mehlhase, S.; Vowinkel, S.; Cherkashinin, G.; Liu, N.; Dietz, C.; Stark, R. W.; Biesalski, M.; Gallei, M. Polymer 2016, 98, 429-436.
- Gallei, M.; Rangou, S.; Filiz, V.; Buhr, K.; Bolmer, S.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1037-1046.
- Schäfer, C. G.; Vowinkel, S.; Hellmann, G. P.; Herdt, T.; Contiu, C.; Schneider, J. J.; Gallei, M. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 7960-7975.